Bortezomib (Velcade®)
On 13 May 2003, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a drug called bortezomib (Velcade®) (formerly known as LDP-341) to treat patients with multiple myeloma, a cancer of plasma cells.
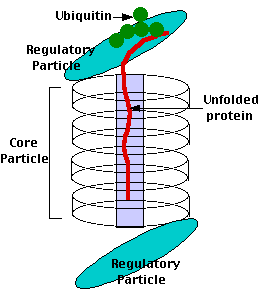
The drug blocks the proteolytic action of the proteasome.
- The failure to degrade IκB blocks the signaling action of the transcription factor NF-κB. [Discussion] Dozens of genes needed for proliferation and adhesion of myeloma cells are turned off.
- The failure to degrade cyclins inhibits completion of the cell cycle and hence the mitotic proliferation of the cancerous cells.
- The drug seems to work especially well when used with conventional chemotherapy drugs probably by inhibiting the ability of the cancer cell to protect itself against the damage "chemo" causes.
- Inhibition of Bcl-2 leads to death of the cell by apoptosis.
- Angiogenesis and metastasis are also inhibited.
The drug is given intermittently, and its action is reversible. Cancer cells are killed while normal cells are spared.
|