| Index to this page |
These factors are described as density-independent because they exert their effect irrespective of the size of the population when the catastrophe struck.
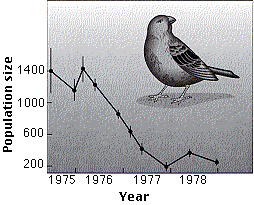
This graph (from P. T. Boag and P.R. Grant in Science, 214:82, 1981) shows the decline in the population of one of Darwin's finches (Geospiza fortis) on Daphne Major, a tiny (100 acres = 40 hectares) member of the Galapagos Islands. The decline (from 1400 to 200 individuals) occurred because of a severe drought that reduced the quantity of seeds on which this species feeds. The drought ended in 1978, but even with ample food once again available the finch population recovered only slowly.
Catastrophic declines are particularly risky for populations living on islands. The smaller the island, the smaller the population of each species on it, and the greater the risk that a catastrophe will so decimate the population that it becomes extinct.

This appears to be one reason for the clear relationship between size of island and the number of different species it contains.
The graph (redrawn from R. H. MacArthur and E. O. Wilson, The Theory of Island Biogeography, Princeton University Press) shows the number of species of reptiles and amphibians on various islands in the West Indies. In general, if one island has 10 times the area of another, it will contain approximately twice the number of species.
The same principle applies to many habitats. In a sense, most habitats are islands. A series of ponds, a range of mountain tops, scattered groves of citrus trees, even individual trees within a grove, all are made up of patches of habitat separated by barriers to the free migration of their inhabitants.
This has practical as well as theoretical importance. As the human population grows, jungles are cleared for agriculture, farms are paved for shopping centers, rivers are dammed for hydroelectric power and irrigation, etc. Although wildlife sanctuaries are being established, they must be made large enough so that they can support populations large enough to survive density-independent checks when they strike.
In 1986, the closing of a dam in Venezuela flooded over a thousand square miles (>2,500 km2) turning hundreds of hilltops into islands. These ranged in size from less than 1 hectare (2.5 acres) to more than 150 hectares (370 acres).

Within 8 years,
Intraspecific competition is competition between members of the same species.
In the summer of 1980, much of southern New England was struck by an infestation of the spongy moth (Lymantria dispar, once known as the gypsy moth). As the summer wore on,Here, then, was a dramatic example of how competition among members of one species for a finite resource — in this case, food — caused a sharp drop in population.

The effect was clearly density-dependent. The lower population densities of the previous summer had permitted most of the animals to complete their life cycle.
The graph shows a similar population crash; in this case of reindeer on two islands in the Bering Sea. Why the population on St. Paul Island went through so much more severe a boom-and-bust cycle than that on St. George Island is unknown.
Many rodent populations (e.g., lemmings in the Arctic) go through such boom-and-bust cycles.When two species share overlapping ecological niches, they may be forced into competition for the resource(s) of that niche. This interspecific competition is another density-dependent check on the growth of one or both populations.

Like so many factors in ecology, interspecific competition is more easily studied in the laboratory than in the field. This graph (based on the work of G. F. Gause) shows the effect of interspecific competition on the population size of two species of paramecia, Paramecium aurelia and Paramecium caudatum.
When either species was cultured alone — with fresh food added regularly — the population grew exponentially at first and then leveled off.
However, when the two species were cultured together, P. caudatum proved to be the weaker competitor. After a brief phase of exponential growth, its population began to decline and ultimately it became extinct. The population of P. aurelia reached a plateau, but so long as P. caudatum remained, this was below the population density it achieved when grown alone.
The habitat of most natural populations is far more complex than a culture vessel. In a natural habitat, the species at a competitive advantage in one part of the habitat might be at a disadvantage in another. In addition, the presence of predators and parasites would limit population growth of the more successful as well as the less successful species. So, in a natural setting, the less effective competitor is usually not driven to extinction.
Declining birth rates also lead to reduced population growth. [Discussion]
We know that humans make deliberate family planning choices, but analogous behavior is found in other animals as well.
An alternative to limiting the number of offspring per pair of parents is to limit the number of parents.
Some mammals and birds achieve this by establishing breeding territories. Each mating pair occupies an area of a size sufficient to supply its needs including those of its offspring. One or both members defend this territory against intrusion from other members of the same species. This behavior not only ensures that the resources on which they depend will not be exceeded but may keep the population in check by preventing breeding among its surplus members.
Social conventions among humans (e.g., attitudes about the proper age of marriage and desirable family size) also have a marked influence on birth rates. However social conventions — and the birth control techniques that may supplement them — have been most successful at reducing birth rates among just those people least in need of it. In the poorer countries, early marriage, a desire for large families, and failure to employ birth control methods reliably are common.| Link to a discussion of human population trends. |

As a population increases, its predators are able to harvest it more easily. These graphs (based on data from Crombie, A. C., Journal of Animal Ecology, 16:44, 1947) show the population changes among flour beetles grown in plain flour (left) and in flour containing pieces of glass tubing.
Each culture was started with four adults of each species. In plain medium, after an initial spurt of both populations, Tribolium continued to expand its numbers while the Oryzaephilus population declined and was eventually driven to extinction (left).
Several factors were at work, but predation was by far the most important.Glass tubing provided a refuge for some Oryzaephilus larvae enabling them to complete their life cycle. This reduction in the intensity of predation permitted the two populations to coexist indefinitely (right).
Parasites are able to pass from host to host more easily as the population density of the host increases. For this reason, epidemics among humans are particularly severe in cities. In fact, for most of the period since humans began living in cities, city populations have been maintained only through continual immigration from the countryside. Not until the development of community sanitation, immunization, and other public health measures did cities avoid periodic sharp drops in population as a result of epidemics.
The recurrent epidemics of the "black death" in Europe that began in the fourteenth century caused a sharp decline in population. In just 3 years (1348–1350), at least one-quarter of the population of Europe died from the disease (probably plague).
More recently, the great influenza pandemic of 1918–1919 is thought to have killed over 20 million people worldwide. [More]
The house finch, Carpodacus mexicanus, — native to western North America — is a recent immigrant to the eastern United States where it is parasitized by a mycoplasma that reduces the lifespan and fecundity of the birds. Data collected by amateur bird watchers show that the arrival of the disease (in the mid-90s) in areas with a high population of the birds drove their numbers down more than it did in regions of low finch populations. Whatever the starting value, all infected populations ended up with similar populations. This is a clear example of the density-dependent effect of parasitism on a population.
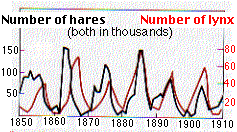
Some populations go through repeated and regular periods of boom followed by bust.
This graph shows the 10-year cyclical fluctuations in the populations (measured by counting the hides offered for sale at the Hudson Bay trading posts in Canada) of the varying hare ("snowshoe rabbit") and its chief predator, the lynx, from 1850 to 1910. The size of the lynx population was closely dependent on the size of its prey (hare) population. The factors causing the hare population to go through its boom-and-bust cycles are still debated, but predation by lynxes was probably only one factor.
Recent field studies have provided clearer answers for three other cyclical populations, voles (a small rodent) in Finland, the red grouse in Scotland, and lemmings (another small rodent) in Greenland.
The vole population in Finland regularly goes through 3-year cycles of boom-and-bust. When Korpimäki and Norrdahl removed all their predators (both mammals and birds) from their test areas, the cycles ceased.
Here, then, the cycles were driven by the density-dependent check of predation.
The red grouse population in Scotland goes through cycles of 4–8 years. From peak to trough, the population may decline by a factor of 1000. These cycles do not appear to be caused by the hunting of this popular game bird.
The birds are parasitized by a nematode, and infected birds have lower fecundity (birth rates down) and higher mortality (death rates up) than uninfected birds.
P. J. Hudson and his colleagues treated large numbers of birds in several test areas with a drug to prevent or cure an infection. The populations in the treatment areas ceased to cycle. It was not necessary to treat all the birds; 20% of them seem enough to prevent epidemics (just as immunization of humans doesn't have to reach 100% to put an end to pathogen transmission).
Here, then, the cycles were driven by the density-dependent check of parasitism.A 15-year study of the population of lemmings in northeast Greenland was reported by Gilg, O., et al., in Science, 31 October 2003. These workers showed that the lemming population rises and falls with a cycle of 4 years. The population of the shorttail weasel (aka ermine, stoat), the principal predator of the lemming, does as well but with a 1-year lag behind the lemming population.
Because of this lag, one might expect that the lemming population would continue to outstrip the weasel population until the lemmings bumped into the carrying capacity of their environment (e.g., availability of food and nesting sites). But this does not occur because as the lemming population grows, other predators (e.g., foxes and owls) shift their diet in favor of lemmings.
As the lemming population then begins to decline,
This graph shows the growth of a yeast population in culture. After a period of exponential growth, the size of the population begins to level off and soon reaches a stable value. This type of growth curve is called sigmoid or S-shaped.
If we add fresh culture medium to the container, exponential growth resumes until a new, higher plateau is reached.
Evidently the growth rate (r) declines as the density of the population approaches a certain limiting value.
| Link to a discussion of the mathematics of population growth. |
When r = 0, dN/dt = 0 and the population ceases to grow. The yeasts have reached zero population growth or ZPG.
The causes:The limiting value of the population that can be supported in a particular environment is called its carrying capacity and is designated K.
When the population is far below K, its growth is exponential, but as the population approaches K, it begins to encounter ever-stronger "environmental resistance". Let us use the expression|
dN = rN
dt | ( | K − N K | ) |
 Although actual populations are unlikely to follow the theoretical logistic growth curve exactly, the curve can provide us with valuable guidance in managing populations.
Although actual populations are unlikely to follow the theoretical logistic growth curve exactly, the curve can provide us with valuable guidance in managing populations.
Example 1: The logistic curve tells you that you are unlikely to rid your house of a large rat population by setting rat traps. No matter how many you put out, the r for rats is so high (perhaps 0.0147 per day) that they will reproduce faster than you can catch them. What you must do instead is to prevent them from getting food in and around your house. With a sharply-reduced K, their population will decline.
Example 2: The converse of the pest problem is how to keep endangered species from becoming extinct. But outlawing hunting will have no appreciable impact if the habitat on which that species depends for its K — pasture or woods or whatever — disappears under the parking lot of a shopping plaza.
Example 3: Modern intensive fishing methods have repeatedly produced ominous declines in the catch of many species as the populations have been unable to maintain themselves. The logistic curve provides a goal to managing fisheries: harvest at only such a rate that the population is maintained at K/2. At this size, the population is able to grow most rapidly. The value K/2 is known as the maximum sustainable yield.
I once plowed up an old field and allowed it to lie fallow. In the first season it grew a large crop of ragweed.
Ragweed is well-adapted to exploiting its environment in a hurry — before competitors can become established. It grows rapidly and produces a huge number of seeds (after releasing its pollen, the bane of many hay fever sufferers).
Because ragweed's approach to continued survival is through rapid reproduction, i.e., a high value of r, it is called an r-strategist. Other weeds, many insects, and many rodents are also r-strategists. If fact, if we consider an organism a pest, it is probably an r-strategist.
In general r-strategists share a number of features:For r-strategists, alleles that enhance any of the traits listed above will be favored by natural selection. Hence, r-strategists are said to be the product of r-selection.

The graph shows 4 representative survivorship curves. The vertical axis gives the fraction of survivors at each age.
When a habitat becomes filled with a diverse collection of creatures competing with one another for the necessities of life, the advantage shifts to K-strategists. K-strategists have stable populations that are close to K. There is nothing to be gained from a high r. The species will benefit most by a close adaptation to the conditions of its environment.
Typically, K-strategists share these qualities:Year 1 = Boom
Year 3 = another Boom year, and so on.
They also found that the population is polymorphic containing:Here, then, intraspecific competition has created a population cycle alternately favoring r-strategists and K-strategists.
| Welcome&Next Search |