All living things must have an unceasing supply of energy and matter. The transformation of this energy and matter within the body is called metabolism.
Catabolism is destructive metabolism. Typically, in catabolism, larger organic molecules are broken down into smaller constituents. This usually occurs with the release of energy (usually as ATP).
Anabolism is constructive metabolism. Typically, in anabolism, small precursor molecules are assembled into larger organic molecules. This always requires the input of energy (often as ATP).
Green plants, algae, and some bacteria are autotrophs ("self-feeders"). Most of them use the energy of sunlight to assemble inorganic precursors, chiefly carbon dioxide and water, into the array of organic macromolecules of which they are made. The process is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis makes the ATP needed for the anabolic reactions in the cell.
All other organisms, including ourselves, are heterotrophs. We secure all our energy from organic molecules taken in from our surroundings ("food"). Although heterotrophs may feed partially (as most of us do) or exclusively on other heterotrophs, all the food molecules come ultimately from autotrophs. We may eat beef but the steer ate grass.
Heterotrophs degrade some of the organic molecules they take in (catabolism) to make the ATP that they need to synthesize the others into the macromolecules of which they are made (anabolism).
 Humans are heterotrophs. We are totally dependent on ingested preformed organic molecules to meet all our energy needs.
We are also dependent on preformed organic molecules as the building blocks to meet our anabolic needs.
Humans are heterotrophs. We are totally dependent on ingested preformed organic molecules to meet all our energy needs.
We are also dependent on preformed organic molecules as the building blocks to meet our anabolic needs.
- Ingestion: taking food within the body (although as the figure shows, it is still topologically in the external world, not the internal).
- Digestion.
The enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of
- Absorption into the body and transport to the cells.
- Absorption into cells
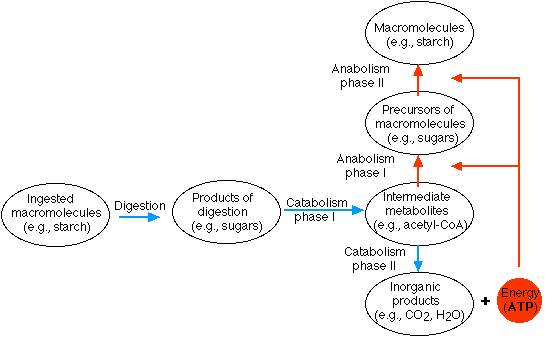
Within cells, these molecules are further degraded into still simpler molecules containing two to four carbon atoms. These fragments (acetyl-CoA for example) face one of two alternatives:
23 May 2010
 Humans are heterotrophs. We are totally dependent on ingested preformed organic molecules to meet all our energy needs.
We are also dependent on preformed organic molecules as the building blocks to meet our anabolic needs.
Humans are heterotrophs. We are totally dependent on ingested preformed organic molecules to meet all our energy needs.
We are also dependent on preformed organic molecules as the building blocks to meet our anabolic needs.
