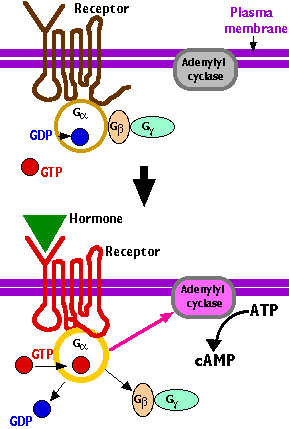
 The three subunits are:
The three subunits are:
In a common example (shown here), the effector molecule is adenylyl cyclase - an enzyme in the inner face of the plasma membrane which catalyzes the conversion of ATP into the "second messenger" cyclic AMP (cAMP) [More].
This type stimulates (s = "stimulatory") adenylyl cyclase. It is the one depicted here. It is associated with the receptors for many hormones such as:
| Gαs is the target of the toxin liberated by Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera. Binding of cholera toxin to Gαs keeps it turned "on". The resulting continuous high levels of cAMP causes a massive loss of salts from the cells of the intestinal epithelium. Massive amounts of water follow by osmosis causing a diarrhea that can be fatal if the salts and water are not quickly replaced. |
This inhibits (i = "inhibitory") adenylyl cyclase lowering the level of cAMP in the cell. Gai is activated by the receptor for somatostatin.
| Link to discussion of the molecular events in vision. |
| Welcome&Next Search |